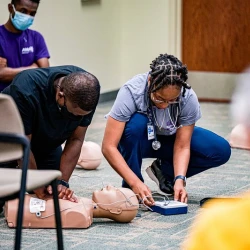
In the realm of emergency medical services (EMS), the role of Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) is critical. EMTs are the first responders on the scene of emergencies, providing vital medical care and assistance to individuals in distress. The nature of their job demands quick thinking, practical skills, and the ability to adapt to rapidly changing situations. One of the foundational aspects of preparing competent and confident EMTs is hands-on training. While theoretical knowledge is undoubtedly essential, the significance of hands-on training in EMT classes cannot be overstated. This article explores the reasons why hands-on training is indispensable in shaping effective EMTs and how it enhances their abilities to provide top-notch care in high-pressure situations.
Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice
Emergency medical situations are often chaotic and unpredictable. While theoretical knowledge equips EMTs with the understanding of medical concepts, it's the practical application of that knowledge that truly prepares them for real-world scenarios. Hands-on training provides the bridge between theory and practice, allowing EMTs to synthesize classroom learning into practical actions. Through hands-on training, students can physically interact with medical equipment, simulate patient assessments, and practice administering treatments. This direct engagement with the tools and techniques they will use in the field enhances their understanding and memory retention, ultimately translating to more effective care delivery.
Skill Refinement and Muscle Memory
In high-stress situations, human performance can be greatly affected. Stress and adrenaline can hinder cognitive function, making it difficult to recall information. This is where muscle memory comes into play. Muscle memory is the result of repetitive actions and practice. By engaging in hands-on training, EMTs develop muscle memory for critical tasks such as CPR compressions, airway management, and splinting. When faced with a real emergency, muscle memory allows EMTs to perform these tasks almost automatically, freeing up cognitive resources to assess the situation and make quick decisions.
Building Confidence and Competence
Confidence is a crucial attribute for EMTs. When individuals are confident in their abilities, they are more likely to make sound decisions under pressure. Hands-on training plays a pivotal role in building this confidence. Through practical exercises and simulations, EMT students gain a sense of competence in their skills. They experience firsthand what it's like to successfully perform procedures, handle equipment, and interact with simulated patients. As they encounter different scenarios during training, they become better equipped to handle various real-life emergencies, fostering a strong sense of self-assuredness.
Realistic Scenario Replication
The beauty of hands-on training lies in its ability to recreate realistic scenarios. Simulation labs, often utilized in EMT training programs, offer a controlled environment where students can practice their skills in scenarios that closely resemble actual emergencies. These simulations range from basic scenarios like assessing a patient's vital signs to complex situations like managing multiple trauma victims at the scene of an accident. Realistic scenario replication not only prepares EMTs for what they might encounter but also allows them to work on their communication and teamwork skills. Collaborating with other trainees, just as they would in real emergencies, enhances their ability to function cohesively in high-pressure situations.
Decision-Making and Critical Thinking
In emergencies, split-second decisions can be a matter of life or death. EMTs must be able to analyze a situation rapidly, prioritize interventions, and adapt to unexpected changes. Hands-on training fosters the development of these decision-making and critical-thinking skills. When faced with a simulated emergency, EMT students must assess the situation, gather information, and decide on appropriate actions. These exercises train them to think on their feet and make informed choices even when the circumstances are challenging.
Communication Skills and Bedside Manner
EMTs don't just provide medical care; they often serve as the primary point of contact between patients, their families, and the healthcare system. Effective communication is key to building rapport, managing patient anxiety, and gathering crucial medical history. Hands-on training offers opportunities for EMTs to practice their communication skills in a controlled setting. Interacting with simulated patients helps them develop empathy, active listening, and the ability to explain procedures and treatments in a clear and reassuring manner. These skills are invaluable in establishing trust and ensuring patients feel supported during distressing situations.
Adapting to Technological Advances
The field of healthcare is constantly evolving, with new technologies and medical advancements emerging regularly. Hands-on training keeps EMTs up-to-date with the latest equipment and techniques. By engaging with cutting-edge medical tools, EMT students become familiar with innovations that can significantly impact patient care. From using portable ultrasound devices to employing advanced airway management equipment, hands-on training ensures that EMTs are well-versed in modern medical practices and can adapt seamlessly to new technologies.
Team Collaboration and Leadership
EMTs rarely work alone. They are part of a broader team that includes fellow EMTs, paramedics, nurses, and physicians. Effective collaboration is essential for providing coordinated care. Hands-on training exposes EMTs to the dynamics of teamwork and encourages them to develop leadership skills. During simulations, they learn how to delegate tasks, communicate clearly within the team, and make decisions that benefit the patient's well-being. These experiences translate directly to real-life emergencies, where effective teamwork can make a significant difference in patient outcomes.
Ethical and Moral Considerations
EMTs often find themselves in ethically and morally complex situations. They may encounter patients who are unable to communicate their wishes, or they might need to make decisions about prioritizing care when resources are limited. Hands-on training can incorporate scenarios that touch on these ethical considerations. This exposure helps EMTs develop the ability to navigate these dilemmas with compassion, empathy, and respect for patient autonomy, ensuring that they uphold the highest ethical standards in their practice.
Conclusion
Hands-on training is the cornerstone of effective EMT education. It transforms theoretical knowledge into practical skills, instills confidence, hones decision-making abilities, and fosters teamwork and communication skills. The controlled environments of simulation labs allow students to experience a wide range of scenarios, preparing them to respond effectively to the unpredictable nature of real emergencies. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, hands-on training ensures that EMTs are equipped with the latest techniques and technologies. Ultimately, the importance of hands-on training in EMT classes cannot be overstated—it is the linchpin that turns individuals into capable, compassionate, and proficient emergency medical technicians.